环境:android13.0.0_r6
1、SystemUI介绍
1.1、SystemUI摘要
1 2 在Android系统中SystemUI是以应用的形式运行在Android系统当中,即编译SystemUI模块会生产APK文件,源代码路径 在frameworks/base/packages/SystemUI/,安装路径system/priv-app/-SystemUI。
1.2、什么是SystemUI
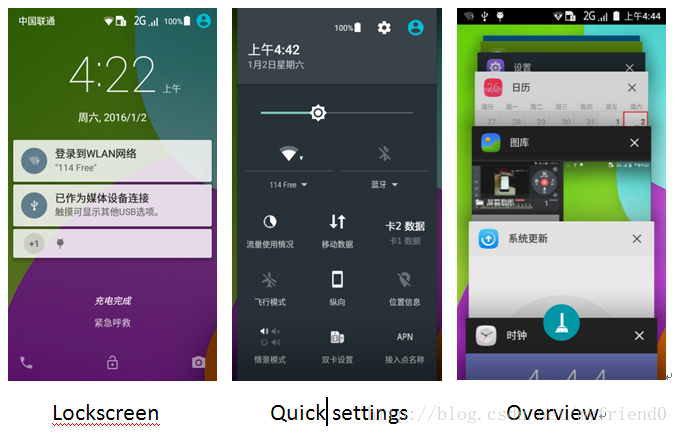
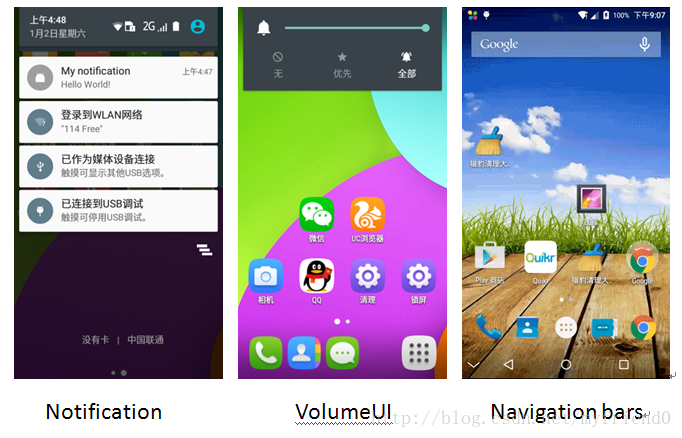
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 在前文1.1章节中可知,SystemUI是一个普通的APK文件,即是一个普通的APP,但是,手机使用者看见的所有SystemUI的内容都不像是 一个APP,为什么?既然是一个应用,就是完成特定的功能,SystemUI主要完成的功能有: (1)、Status bars (2)、Navigation bars (3)、Notification (4)、Lockscreen (5)、Quick settings (6)、Overview(recent task switcher) (7)、VolumeUI
2、SystemUI的架构
SystemUI的整体架构:
Android SystemUI采用了MVC(Model-View-Controller)架构,以实现界面元素的管理和交互。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 状态栏(Status Bar):显示系统状态信息,如时间、电池电量、信号强度等,并提供快速访问通知和快捷设置的入口。 导航栏(Navigation Bar):提供设备导航和操作控制,包括返回、主页和最近任务等按钮。 通知管理器(Notification Manager):负责接收、管理和展示通知,包括应用推送的通知和系统事件的通知。 快捷设置(Quick Settings):提供快速访问常用系统设置的面板,如Wi-Fi、蓝牙、亮度等,以方便用户进行快速调整。 锁屏界面(Lock Screen):显示在设备锁定状态下的界面,提供时间、日期、通知预览和快速启动应用等功能。 系统UI控制器(System UI Controller):作为整个SystemUI的控制中心,负责协调各个组件之间的交互和管理。 其他辅助组件:还有一些辅助组件,如电源管理器、音量控制器等,用于管理设备的电源和音量控制。
这些组件相互配合,构成了SystemUI的整体架构。每个组件负责不同的功能和交互,并通过事件触发和消息传递等机制相互关联。理解SystemUI的架构和组件之间的相互关系,有助于我们深入了解系统界面的实现原理,并进行自定义和扩展。
3、SystemUI的启动过程
SystemUI任何内容都不像一个APP,自然它的启动也不像大多APP一样启动一个Activity。SystemUI顾名思义就是全局UI,必须在开机过程中完成启动,并不可退出。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Android系统启动流程: 1.按下电源,系统上电 2.从固定地址启动固化在ROM的BootLoader程序 3.启动Linux内核,加载init进程 4.启动init进程,fork出zygote进程 5.启动SystemServer,启动Binder线程池以及各种服务 6.AMS启动Launcher, 然后你就看到该看到的了
SystemUI作为系统主要进程,就是在SystemServer启动的服务其中之一
SystemServer.java
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 public static void main (String[] args) { new SystemServer ().run(); } private void run () { ...... try { traceBeginAndSlog("StartServices" ); startBootstrapServices(); startCoreServices(); startOtherServices(); SystemServerInitThreadPool.shutdown(); } catch (Throwable ex) { Slog.e("System" , "******************************************" ); Slog.e("System" , "************ Failure starting system services" , ex); throw ex; } finally { traceEnd(); } ...... } private void startOtherServices () { ...... mActivityManagerService.systemReady(() -> { Slog.i(TAG, "Making services ready" ); traceBeginAndSlog("StartActivityManagerReadyPhase" ); ...... try { startSystemUi(context, windowManagerF); } catch (Throwable e) { reportWtf("starting System UI" , e); } ...... } } static final void startSystemUi (Context context, WindowManagerService windowManager) { PackageManagerInternal pm = LocalServices.getService(PackageManagerInternal.class); Intent intent = new Intent (); intent.setComponent(pm.getSystemUiServiceComponent()); intent.addFlags(Intent.FLAG_DEBUG_TRIAGED_MISSING); context.startServiceAsUser(intent, UserHandle.SYSTEM); windowManager.onSystemUiStarted(); }
总结下代码流程:SystemServermain()方法会调用SystemServer.run()方法,在run方法中,会启动bootStrapService,coreService,以及其他服务otherService,在startOtherServices()中,会注册AMS的systemReady回调,在回调中启动SystemUI,其实就是启动了SystemUIService。
SystemUIService.java
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 @Override public void onCreate () { super.onCreate (); ((SystemUIApplication) getApplication ()).startServicesIfNeeded (); ..... }
SystemUIApplication.java
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 //frameworks/base/packages/SystemUI/src/com/android/systemui/SystemUIApplication.java public void startServicesIfNeeded() { final String vendorComponent = SystemUIFactory.getInstance() .getVendorComponent(getResources()); // Sort the startables so that we get a deterministic ordering. // TODO: make #start idempotent and require users of CoreStartable to call it. Map<Class<?>, Provider<CoreStartable>> sortedStartables = new TreeMap<>( Comparator.comparing(Class::getName)); sortedStartables.putAll(SystemUIFactory.getInstance().getStartableComponents()); sortedStartables.putAll(SystemUIFactory.getInstance().getStartableComponentsPerUser()); startServicesIfNeeded( sortedStartables, "StartServices", vendorComponent); }
SystemUIApplication.java
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 private void startServicesIfNeeded ( Map<Class<?>, Provider<CoreStartable>> startables, String metricsPrefix, String vendorComponent) if (mServicesStarted) { return ; } mServices = new CoreStartable[startables.size () + (vendorComponent == null ? 0 : 1 )]; if (!mBootCompleteCache.isBootComplete ()) { if ("1" .equals (SystemProperties.get ("sys.boot_completed" ))) { mBootCompleteCache.setBootComplete (); if (DEBUG) { Log.v (TAG, "BOOT_COMPLETED was already sent" ); } } } mDumpManager = mSysUIComponent.createDumpManager (); Log.v (TAG, "Starting SystemUI services for user " + Process.myUserHandle ().getIdentifier () + "." ); TimingsTraceLog log = new TimingsTraceLog ("SystemUIBootTiming" , Trace.TRACE_TAG_APP); log.traceBegin (metricsPrefix); int i = 0 ; for (Map.Entry<Class<?>, Provider<CoreStartable>> entry : startables.entrySet ()) { String clsName = entry.getKey ().getName (); int j = i; timeInitialization ( clsName, () -> mServices[j] = startStartable (clsName, entry.getValue ()), log, metricsPrefix); i++; } if (vendorComponent != null) { timeInitialization ( vendorComponent, () -> mServices[mServices.length - 1 ] = startAdditionalStartable (vendorComponent), log, metricsPrefix); } for (i = 0 ; i < mServices.length; i++) { if (mBootCompleteCache.isBootComplete ()) { mServices[i].onBootCompleted (); } mDumpManager.registerDumpable (mServices[i].getClass ().getName (), mServices[i]); } mSysUIComponent.getInitController ().executePostInitTasks (); log.traceEnd (); mServicesStarted = true ; }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 <!-- SystemUI Services: The classes of the stuff to start. --> <string-array name="config_systemUIServiceComponents" translatable="false" > <item>com.android.systemui.Dependency</item> <item>com.android.systemui.util.NotificationChannels</item> <item>com.android.systemui.statusbar.CommandQueue$CommandQueueStart</item> <item>com.android.systemui.keyguard.KeyguardViewMediator</item> <item>com.android.systemui.recents.Recents</item> <item>com.android.systemui.volume.VolumeUI</item> <item>com.android.systemui.stackdivider.Divider</item> <item>com.android.systemui.SystemBars</item> <item>com.android.systemui.usb.StorageNotification</item> <item>com.android.systemui.power.PowerUI</item> <item>com.android.systemui.media.RingtonePlayer</item> <item>com.android.systemui.keyboard.KeyboardUI</item> <item>com.android.systemui.pip.PipUI</item> <item>com.android.systemui.shortcut.ShortcutKeyDispatcher</item> <item>@string/config_systemUIVendorServiceComponent</item> <item>com.android.systemui.util.leak.GarbageMonitor$Service</item> <item>com.android.systemui.LatencyTester</item> <item>com.android.systemui.globalactions.GlobalActionsComponent</item> <item>com.android.systemui.ScreenDecorations</item> <item>com.android.systemui.fingerprint.FingerprintDialogImpl</item> <item>com.android.systemui.SliceBroadcastRelayHandler</item> </string-array> <!-- SystemUI vender service, used in config_systemUIServiceComponents. --> <string name="config_systemUIVendorServiceComponent" translatable="false" >com.android.systemui.VendorServices</string>
SystemUIService的onCreate()方法中,直接调用SystemUIApplication.startServicesIfNeeded()方法,最终会将所有服务一一加载并通过start()方法启动起来。
至此,SystemUI基本启动流程就结束了。