主要分析一下SystemServer启动过后的内部逻辑,特别说明一下AMS ,WMS都属于SystemServer进程,属于同一个进程
一. SystemServer进程启动流程 基于Android13的系统启动流程分析(五)之Zygote和SystemServer启动流程 这篇文章有详细讲解,这里再简单的过一下如何启动的SystemServer
在zygote进程创建过后,会调用forkSystemServer()来孵化出SystemServer进程,当前该进程创建成功后会反射调用到SystemServer.java的main函数,从而启动完成SystemServer
二. SystemServer主函数分析 main函数会被ZygoteInit的子方法handleSystemServerProcess反射调用到
public static void main(String[] args) {
new SystemServer().run();
}
继续看看run方法
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 private void run () ... try { ... if (!SystemProperties.get ("persist.sys.language" ).isEmpty ()) { final String languageTag = Locale.getDefault ().toLanguageTag (); SystemProperties.set ("persist.sys.locale" , languageTag); SystemProperties.set ("persist.sys.language" , "" ); SystemProperties.set ("persist.sys.country" , "" ); SystemProperties.set ("persist.sys.localevar" , "" ); } ... android.os.Process.setThreadPriority ( android.os.Process.THREAD_PRIORITY_FOREGROUND); android.os.Process.setCanSelfBackground (false ); Looper.prepareMainLooper (); Looper.getMainLooper ().setSlowLogThresholdMs ( SLOW_DISPATCH_THRESHOLD_MS, SLOW_DELIVERY_THRESHOLD_MS); ... System.loadLibrary ("android_servers" ); ... createSystemContext (); ActivityThread.initializeMainlineModules (); ServiceManager.addService ("system_server_dumper" , mDumper); mDumper.addDumpable (this ); mSystemServiceManager = new SystemServiceManager (mSystemContext); mSystemServiceManager.setStartInfo (mRuntimeRestart, mRuntimeStartElapsedTime, mRuntimeStartUptime); mDumper.addDumpable (mSystemServiceManager); LocalServices.addService (SystemServiceManager.class , mSystemServiceManager); ... try { t.traceBegin ("StartServices" ); startBootstrapServices (t); startCoreServices (t); startOtherServices (t); } catch (Throwable ex) { ... } finally { ... } ... Looper.loop (); throw new RuntimeException ("Main thread loop unexpectedly exited" ); }
以上方法可以看出来关于其他服务的启动都是运行在主线程中的Looper.prepareMainlooper~ Looper.loop之间,每个SystemServer中的服务都有一个binder ,会加入到ServiceManager的binder线程池中统一管理,这样拿到全局的ServiceManager,根据AIDL 获取到每Service了
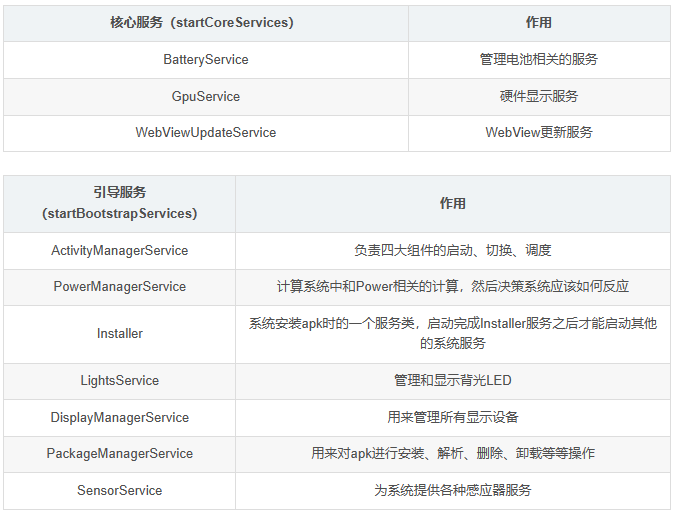
startBootstrapServices(t)
startCoreServices(t)
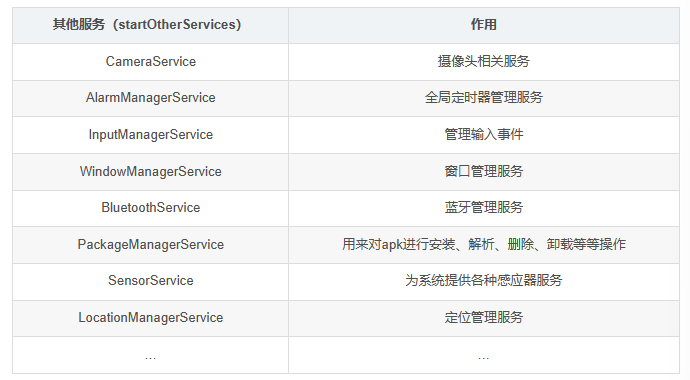
startOtherServices(t)
在这些启动的服务里(调用了onStart启动服务),都会将服务存入ServiceManager 用来管理系统中的各种Service,用于系统C/S架构中的Binder机制通信:Client端要使用某个Service,则需要先到ServiceManager查询Service的相关信息,然后根据Service的相关信息与Service所在的Server进程建立通讯通路,这样Client端就可以使用Service了
1. startBootstrapServices 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 private void startBootstrapServices (@NonNull TimingsTraceAndSlog t) t.traceBegin ("StartWatchdog" ); final Watchdog watchdog = Watchdog.getInstance (); watchdog.start (); t.traceEnd (); ... t.traceBegin ("StartInstaller" ); Installer installer = mSystemServiceManager.startService (Installer.class ); t.traceEnd (); ... t.traceBegin ("UriGrantsManagerService" ); mSystemServiceManager.startService (UriGrantsManagerService.Lifecycle.class ); t.traceEnd (); t.traceBegin ("StartPowerStatsService" ); mSystemServiceManager.startService (PowerStatsService.class ); t.traceEnd (); ... t.traceBegin ("StartActivityManager" ); ActivityTaskManagerService atm = mSystemServiceManager.startService ( ActivityTaskManagerService.Lifecycle.class ).getService (); mActivityManagerService = ActivityManagerService.Lifecycle.startService ( mSystemServiceManager, atm); mActivityManagerService.setSystemServiceManager (mSystemServiceManager); mActivityManagerService.setInstaller (installer); mWindowManagerGlobalLock = atm.getGlobalLock (); t.traceEnd (); ... t.traceBegin ("StartPowerManager" ); mPowerManagerService = mSystemServiceManager.startService (PowerManagerService.class ); t.traceEnd (); ... t.traceBegin ("StartLightsService" ); mSystemServiceManager.startService (LightsService.class ); t.traceEnd (); t.traceBegin ("StartDisplayManager" ); mDisplayManagerService = mSystemServiceManager.startService (DisplayManagerService.class ); t.traceEnd (); ... mPackageManagerService = PackageManagerService.main (mSystemContext, installer, domainVerificationService, mFactoryTestMode != FactoryTest.FACTORY_TEST_OFF, mOnlyCore); } finally { Watchdog.getInstance ().resumeWatchingCurrentThread ("packagemanagermain" ); } ... t.traceBegin ("StartSensorService" ); mSystemServiceManager.startService (SensorService.class ); t.traceEnd (); t.traceEnd (); }
可以看到大多数服务都是通过mSystemServiceManager.startService来启动,核心服务和其他服务都是一样的,就不过多分析了
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 public <T extends SystemService> T startService (Class<T> serviceClass) { try { final String name = serviceClass.getName (); ... final T service; try { Constructor<T> constructor = serviceClass.getConstructor (Context.class ); service = constructor.newInstance (mContext); } ... startService (service); return service; } finally { Trace.traceEnd (Trace.TRACE_TAG_SYSTEM_SERVER); } } public void startService (@NonNull final SystemService service) mServices.add (service); long time = SystemClock.elapsedRealtime (); try { service.onStart (); } catch (RuntimeException ex) { ... } warnIfTooLong (SystemClock.elapsedRealtime () - time, service, "onStart" ); }
可以看到startService方法就是反射拿到服务类,然后加入队列中,调用其onStart方法进行启动
2. ServiceManager服务管理 每个属于SystemServer的服务都将加入到ServiceManager的binder线程池中,以供后续直接获取和管理
1 mSystemServiceManager.startService (BatteryService.class );
已知startService后会调用BatteryService服务的onStart方法,继续看看onStart内部
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 @Override public void onStart () { ... mBinderService = new BinderService (); publishBinderService ("battery" , mBinderService); mBatteryPropertiesRegistrar = new BatteryPropertiesRegistrar (); publishBinderService ("batteryproperties" , mBatteryPropertiesRegistrar); publishLocalService (BatteryManagerInternal.class , new LocalService ()); }
继续看看mBinderService具体是什么,又是如何加入到ServiceManager中的
1 2 3 private final class BinderService extends Binder { ... }
可以看到mBinderService就是一个Binder,然后调用publishBinderService加入到ServiceManager中的binder线程池中
1 2 3 protected final void publishBinderService (...) ServiceManager.addService (name, service, allowIsolated, dumpPriority); }
调用ServiceManager.addService加入到binder线程池中(ServiceManager暂不深究,只知其内部维护了binder线程池),而ServiceManager服务早就在rc文件中作为核心服务启动了,所以具体实现都是c++代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 service servicemanager /system/bin/servicemanager class core animation user system group system readproc critical onrestart restart apexd onrestart restart audioserver onrestart restart gatekeeperd onrestart class_restart main onrestart class_restart hal onrestart class_restart early_hal writepid /dev/cpuset/system-background/tasks shutdown critical
三. 总结 其实SystemServer是通过init fork出来的,父进程就是zygote,而zygote父进程就是init进程。WMS ,PMS,电池服务,蓝牙服务等。这些服务都不是单独的进程,而是都属于SystemServer进程,启动这些服务过后会将这些服务加入ServiceManager的binder线程池中,因为这些服务内部都创建了Binder实例,再加入到了ServiceManager的binder线程池中,以便与随时获取服务与只通信
参考文章:Android系统启动流程(三)解析SyetemServer进程启动过程